New Reasons to Eat More Whole Grains and Fiber
Take a look in your pantry. Do you see whole-grain pasta? Does the label on your bread say 100% whole wheat? (Are you sure? Dont be fooled by terms like multigrain.) Is your breakfast cereal made with whole grains?We are very fortunate these days-for almost any type of baked product there is a whole-grain option that one can choose in place of the refined-grain option, says Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, director of Tufts HNRCA Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory. Just be careful; dont try to judge whether something is made from whole grain by its color. It is important to read the label the first time, just to make certain. Some light-colored products are made with white whole grains and some dark-colored products are not and just appear so because caramel or other coloring was added.
Staying Highly Fit Slows Signs of Aging
Older people who are highly fit, such as recreational cyclists, are physiologically more similar to young people than to more sedentary seniors. Thats the conclusion of a new British study that sought to explore the effect of physical activity on key indicators of aging. As one scientist put it, Being physically active makes your body function on the inside more like a young persons.
Cutting Away Mold on Fruit: Is it Safe?
Molds are microscopic fungi that live on plant or animal matter, which can sometimes be seen with the naked eye. These organisms give off spores, which are responsible for their color. While many molds are harmless and beneficial, such as cheese, some molds cause allergic reactions and respiratory problems. Similarly, a few molds, under the right conditions, produce mycotoxins-poisonous substances that can make you sick. In many foods, mold invades deep within the food-not just on the surface. In some cases, toxins may have spread throughout the food.
FDA Rejects Aspartame-Ban Petitions
Despite a drumbeat of bad press for aspartame, the US Food and Drug Administration says theres no new credible scientific evidence to change the agencys position that the zero-calorie sweetener is safe for the general population. The FDA recently rejected two citizen petitions calling for an aspartame ban. The agency noted it had analyzed 195 reports of supposed aspartame-related side effects over a 10-year span and did not identify any causal link between aspartame consumption and the reported adverse events or an established mechanism that would explain how aspartame is associated with the reported adverse events.
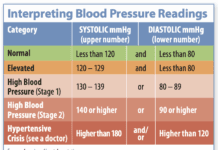
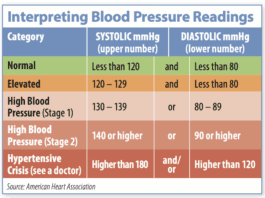
Behind The Numbers
What do those blood-pressure numbers mean? Blood pressure is typically recorded as two numbers, each measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). The numbers reflect how high the pressure pushes a column of mercury in a device called a sphygmomanometer (much as the mercury rises in a thermometer in response to heat).
New Research on High Blood Pressure: What You Need to Know
About one in three American adults, some 67 million people, have high blood pressure, one of the most dangerous risk factors for stroke. If youre age 65 years or older, the odds are even greater that you have hypertension: 64% of men and 69% of women ages 65 and up have high blood pressure, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Putting B Vitamins for Brain Protection to the Test
Could extra B vitamins reduce your risk of cognitive decline and dementia by lowering blood levels of an amino acid called homocysteine? That tantalizing promise was put to the test in two recent large-scale studies, and in both cases researchers proclaimed the results disappointing. But other experts say the jury is still out, particularly for people with low B-vitamin status or those who are already experiencing cognitive decline.
How Good Is Glycemic Index as a Marker of a Heart-Healthy Diet?
Does the glycemic index of the foods you eat matter? Thats the question raised by a headline-making new study sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, the OmniCarb study, which calls into question the notion of good carbs versus bad carbs. Some previous research-along with popular diet plans-suggested that its healthier to choose carbohydrate sources that raise blood sugar levels slowly. These low-glycemic index foods include most whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, as opposed to high-glycemic options such as white bread, potatoes and sugary foods.
Replacing Saturated Fat with Vegetable Oil Linked to Lower Heart Risk
If youve been confused by recent headlines suggesting Butter Is Back and studies questioning the link between saturated fat and heart disease, a new meta-analysis may set the record straight. The research found that people who swap 5% of the calories they consume from saturated fat sources such as red meat and butter with foods containing linoleic acid-the main polyunsaturated fat found in vegetable oil, nuts and seeds-was associated with a 9% lower risk of coronary heart disease events. Switching from saturated fat to linoleic acid was also associated with a 13% lower coronary heart disease mortality risk.
FDA Cracks Down on Coconut Claims
Products containing coconut, coconut oil and coconut milk are popping up everywhere, with marketers touting coconut as the latest superfood. But a recent warning letter from the US Food and Drug Administration cautions coconut boosters not to overreach. The FDA warned that coconut products cant be labeled as healthy if they contain more than 1 gram of saturated fat or more than 15% of calories come from saturated fat. Some have claimed that the saturated fat in coconut is different because its mostly lauric acid, which a few small studies suggest is metabolized differently than other saturated fats. But the FDA isnt buying that argument, noting that coconut products might contain as much as 16 grams of saturated fat per serving.