T cells – Definition – T cells, or lymphocytes, are white blood cells that comprise part of the immune system and help fight off harmful substances. Relevance – Abnormal levels of T cells are associated with lymph node and immunodeficiency disorders; high T cell levels can be caused by infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis, and other diseases, while low T cells may be caused by HIV, AIDS, aging, cancer, radiation, and other diseases.
Tannins – Definition – Tannins are polyphenols that are water-soluble and found in many plants that often confer a bitter taste. Relevance – Tannins are found in the skin of grapes, and therefore, red wine, but also tea, nuts, berries, legumes, and some herbs; they are astringent and cause dryness in the mouth and may confer some of the health benefits of polyphenols.
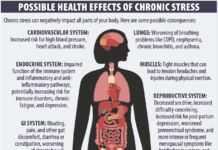
Telomeres – Definition – Sections of DNA that protect the ends of our chromosomes, similar to how plastic tips protect the ends of shoelaces. Relevance – Shortened telomere length is associated with cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, major cancers and shorter life expectancy.
Thiamin – Definition – Thiamin, or vitamin B1, is a water-soluble vitamin that helps supply the brain and nervous system with energy via carbohydrates and is found in grains, beef liver, eggs, legumes, nuts and seeds. Relevance – Thiamin is found in enriched, fortified and whole grain products because the FDA requires food manufacturers to add thiamin to enriched bread, cereal and grain products to prevent deficiency diseases, such as beriberi.
Thymol – Definition – Thymol is a phenol compound found in thyme. Relevance – Thymol is used as an antiseptic and a stabilizer in pharmaceuticals.
Tolerable upper level – Definition – The maximum amount of a nutrient that is unlikely to pose health risks for most healthy people in a given age and gender group. Levels are set by the National Academy of Medicine. Relevance – As someone’s intake increases above the tolerable upper level (upper limit), the potential for adverse health effects increases, particularly if exceeded regularly.
Total cholesterol to HDL ratio – Definition – Calculated by dividing the total cholesterol level by the HDL cholesterol level. For example, if your total cholesterol is 250 and your HDL is 50, the ratio would be 5 to 1. Relevance – For heart health, the goal is to keep the ratio below 5 to 1. The optimum ratio is 3.5 to 1.
Trans fat – Definition – Trans fatty acids are manufactured via hydrogenation, which extends the shelf life of polyunsaturated oils to keep them solid at room temperature and prevent rancidity. Relevance – Hydrogenated fats have no known health benefits and are found in margarine, commercial baked goods, highly processed food, fast-food, and fried food. Increasingly banned, trans fats are dangerous to heart health, increasing the risk of heart disease, heart attack, LDL cholesterol, certain cancers and premature cardiovascular death.
Transcobalamin – Definition – A protein that transports vitamin B12 from the intestines to the body’s tissues. Relevance – An estimated 20% of the population has two copies of a variant in a gene known as TCN2, which decreases how much transcobalamin is made and its ability to bind to vitamin B12. That increases risk of B12 deficiency.
Triglycerides – Definition – Triglycerides are a fat that circulates in the blood that are used for energy and are composed of three fatty acids and a glycerol backbone. Relevance – High triglyceride levels increase the risk of heart disease and metabolic syndrome, which includes high blood pressure, presence of fat mass around the abdomen, poor cholesterol levels (high LDL and low HDL) and increased blood sugar.
Triglyceride to HDL ratio – Definition – Calculated by dividing triglycerides by the HDL cholesterol level. For example, if your triglycerides are 200 and your HDL is 50, the ratio would be 4 to 1. Relevance – A ratio of triglycerides to HDL cholesterol of 3 to 1 or higher has a close correlation to insulin resistance in some populations (so it may be used as an indirect measure of insulin resistance).
Type-2 diabetes – Definition – Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the body does not use insulin effectively, disrupting the way the body metabolizes glucose (sugar), the body’s main fuel. Relevance – Type 2 diabetes develops over time and causes insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar. Although there is no cure, type 2 diabetes can often be controlled by exercising, eating well, maintaining a healthy weight, or medication; particularly if diet and exercise alone don’t control blood sugar.
Tyramine – Definition– Tyramine is a chemical found naturally in high amounts in aged or fermented foods, especially aged cheeses, cured meats, certain beers, and some improperly stored high-protein foods. Relevance – Tyramine is widely believed to trigger migraines and people taking certain antidepressants (MAO inhibitors) cannot break down tyramine properly, which allows it to enter the bloodstream, where it can cause high blood pressure.