C-reactive protein – Definition – Made in the liver, C-reactive protein (CRP) is a biomarker that indicates inflammation throughout the body when blood levels are high. Relevance – CRP tests are administered to determine if there is inflammation in the body or if anti-inflammatory medication is working properly; positive results indicate inflammation, which could be caused by numerous conditions.
Calcium– Definition – Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and essential for nerve transmission, cell signaling, muscle contraction, vascular contraction, hormone secretion, and bone health. Relevance – 99% of the body’s calcium supply is stored in the bones, and the balance of calcium being reabsorbed and deposited changes with age so that bone breakdown exceeds bone formation, resulting in bone loss that can lead to osteoporosis.
Calcium channel blockers – Definition – Calcium channel blockers are drugs used to manage high blood pressure, heart arrhythmia, and angina that slow the entrance of calcium into the heart muscle, relaxing the vessels to improve blood flow. Relevance – There are numerous types of calcium channel blockers, and the action of several of them are negatively affected by grapefruit and grapefruit juice, as well as alcohol, so it is critical to avoid both if taking one of the calcium channel blockers affected by them.
Cardiometabolic disease – Definition – Collectively refers to coronary heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes. Relevance – Following a healthy dietary pattern and lifestyle may significantly reduce risk of cardiometabolic disease and premature death related to these conditions.
Carotenoid – Definition – Carotenoids are pigments produced in plants that give some fruits and vegetables their yellow,red, and orange colors such as carrots, green leafy vegetables, and sweet potatoes. Relevance – Carotenoids are free radical-fighting antioxidants that are being studied in cancer prevention and some carotenoids are converted to Vitamin A in the body.
Carvacrol – Definition – Carvacol is a phenol derived from oregano that is responsible for its biological activity. Relevance – Carvacrol is reported to be antimicrobial, and protective against tumors, inflammation, and kidney disease.
Casein – Definition – Casein is a protein found in milk and milk products. Relevance -Casein is one of the main components used to make cheese and foods containing casein are high in calcium and phosphorus; it is sometimes eliminated using exclusion diets for children with autism as part of a complementary medicine approach, but the research is not strong.
Catechins – Definition -Catechins are compounds belonging to the flavanol group of phytochemicals that are found in red wine, green tea extract, grapes, strawberries, and apricots. Relevance – Catechins have been associated with increased antioxidant activity, fat oxidation and blood vessel dilation, and some studies have found catechin intake to be linked with decreased body mass index, LDL cholesterol and blood pressure.
Causal relationship – Definition – A cause and effect relationship in which a specific variable causes a certain effect. Relevance – Observational (epidemiological) studies cannot prove that a specific variable causes a certain effect; such studies can only suggest there’s a relationship between the two.
Celiac disease – Definition – Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease in which the body targets and launches an immune response in the small intestine on gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye. Relevance -The immune response brought on by gluten intake causes inflammation that eventually damages the lining of the small intestine, causing nutrient malabsorption, bloating, and weight loss; if prolonged, the brain and nervous system can suffer.
Chlorogenic acid – Definition – Chlorogenic acid is a polyphenol plant compound found in coffee beans that is broken down when the beans are roasted. Relevance – Chlorogenic acid has had media attention recently for its alleged capability to incur weight loss and improve glucose tolerance when consumed as green coffee bean extract.
Cholesterol – Definition – Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance produced in the body and obtained through intake of animal products that is used to make hormones, digestive enzymes and vitamin D in the body. Relevance – The body produces all the cholesterol it needs and cholesterol is carried through the bloodstream by low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). It is important to have healthy levels of both, because when there is too much cholesterol in the blood, it builds up in the arteries and increases the risk of developing heart disease.
Choline – Definition – An essential nutrient found in a wide variety of foods. In the US, the most common sources are meat, poultry, fish, dairy products and eggs. It’s also found in cruciferous vegetables, beans, nuts, seeds and whole grains (particularly quinoa). Relevance – Choline is used by your brain and nervous system to help regulate memory, mood and muscle control.
Cirrhosis – Definition – Scarring of the liver, typically because of injury or long-term disease. Relevance – Scarred liver tissue does not function as well, such as in processing nutrients from food, making new proteins and cleaning the blood. The most common causes of cirrhosis are alcoholism and hepatitis (viral infection). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (associated with obesity) is the third most common cause of cirrhosis in the US.
Coenzyme Q10 – Definition – Coenzyme Q10 is a substance produced in the body that is vitamin-like and found in high amounts in the heart, kidneys, liver, and pancreas. Relevance – Coenzyme Q10 is used to treat congestive heart failure, angina, hypertension and other heart conditions; it is also used to treat diabetes, gum disease, Lyme disease, breast cancer and many other conditions.
Colorectal cancer – Definition – Cancer that occurs in the colon (large intestine) or rectum (the passageway from the colon to the anus). Relevance – It is the second leading cancer killer and occurs most often in people ages 50 and older.
Constipation – Definition– May be characterized by frequent straining during bowel movements, lumpy or hard stools, feeling like you didn’t eliminate everything during a bowel movement and/or having fewer than three bowel movements in a week. Relevance – Eating fiber-rich plant foods (fruites, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts and seds), good hydration and regular exercise may help precent constipation.
Copper – Definition – Copper is a trace mineral that is essential to the body and found in all tissues. Relevance – Copper, along with iron, helps produce red blood cells and supports nerve, bone, blood vessel and immune health; copper is found in shellfish, whole grains, beans, nuts, and organ meats.
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) score – Definition – An indicator of how much total plaque (fatty deposits) someone has in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. Relevance – The more the score increase above zero, the greater the risk of coronary heart disease. CAC scores higher than 100 are associated with a high risk of a coronary heart disease event with 2 to 5 years.
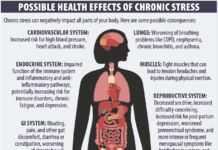
Cortisol – Definition – Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the body’s adrenal glands during stress that stimulates the breakdown of body proteins for energy. Relevance – Cortisol levels are optimally high in the morning and wane throughout the day; high baseline cortisol is associated with abdominal fat and can cause sleep problems, increased appetite, cravings for sugar and fat.
Coumarin – Definition – A naturally-occurring phytochemical that has blood thinning actions. Relevance – Cinnamon spice is high in coumarin, particularly the common Cassia variety sold in spice jars and often used in supplements. High intake of cinnamon could potentially cause excessive bleeding in someone on blood thinning medication.
Crohn’s disease – Definition – Crohn’s disease is an irritable bowel disease (IBD) characterized by inflammation, irritation, or swelling of the digestive tract causing pain and sometimes scar tissue build-up due to chronic inflammation. Relevance – The cause of Crohn’s disease is not well understood, but some research suggests that it may be caused by an unusual immune response by the body.
Cross-reactivity – Definition – When the immune system sees similar protein structures in related foods (or other allergens), potentially resulting in an allergic reaction to either. Relevance – As an example, people allergic to one type of tree nut may be allergic to others. Cross reactions between food and non-food allergens, such as pollens or latex, also are possible.
Cruciferous – Definition – Cruciferous vegetables contain chemicals known as glucosinolates, as well as vitamins, minerals and other nutrients; they include broccoli, arugula, kale, radishes, cauliflower, cabbage, collard greens, turnips, Brussels sprouts, among others. Relevance – The glucosinolates in cruciferous vegetables are responsible for their bitter flavor and may be protective against cancer when they are broken down into active compounds, including indoles and isothiocyanates.
Curcumin – Definition – Curcumin is a large component of the spice turmeric that is a natural phenol compound responsible for the spice’s yellow-gold color. Relevance – Curcumin, as part of turmeric, is used to treat arthritis, stomach acid problems, stomach bloating, headaches and a vast array of other conditions related to pain and inflammation.