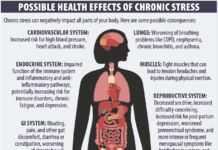
Gait – Definition – The process of walking. Relevance – As a person ages, gait (walking) speed can be used as an indicator of things like long-term risk of falling, breaking a bone, being hospitalized and ultimately, how much longer a person will likely live.
Garlic scapes – Definition – Spindly vegetables that are the green shoots that grow from garlic bulbs. Relevance – Their flavor is similar to garlic cloves but milder. They can be served as a vegetable (such as steamed or grilled) or chopped and used as a seasoning for dishes.
Genetic variant – Definition – An alteration from the most common genetic (DNA) sequence. In the past, the term “mutation” was more commonly used than variant. Relevance – The alteration may not cause any harmful effects, or it may contribute to disease. In some cases the significance of variants isn’t known.
GERD – Definition – Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition that results from the backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus, causing heartburn, irritation of the esophagus, and other symptoms. Relevance – Risk factors for GERD include alcohol intake, obesity, pregnancy, smoking, and certain medical conditions, although many medications can cause or exacerbate heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux.
Gingivitis – Definition – A type of periodontal (gum) disease characterized by gum inflammation, redness, swelling and a tendency to bleed. Relevance – It may be due to various factors such as poor dental hygiene or poorly fitting dentures. If untreated, gingivitis may progress to periodontitis, a more severe type of periodontal disease.
Ginkgo biloba – Definition – Ginkgo biloba is an herb from an ancient tree species that has been used for millennia as a medicinal treatment. Relevance – Ginkgo biloba acts as an antioxidant and shows some effectiveness in treating certain forms of dementia; it improves blood flow in the brain and may boost memory and cognition.
Ginseng – Definition – Ginseng is a root that has been used medicinally for millennia in China; it exists in several forms (American, Asian, and Siberian), but Siberian ginseng is a different plant that lacks the health-enhancing compounds. Relevance – The active ingredients in ginseng are believed to be ginsenosides, which may reduce the risk of cold and flu, improve mental performance and decrease stress.
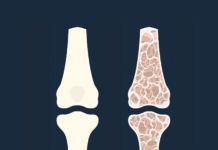
Glucosamine – Definition – Glucosamine is found naturally in the body, particularly in the fluid surrounding joints, but it can also be harvested from shellfish shells or made synthetically. Relevance – Glucosamine is windily used to treat arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, as glucosamine sulfate.
Gluten – Definition – Gluten is a protein found in grains like wheat, barley and rye. Relevance – Gluten-free diets are used to treat Celiac disease, but have become popular for many people who claim to have gluten sensitivities; there are no adverse health effects linked to gluten intake in people without Celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
Glycemic index – Definition – A scale of 0 to 100 that ranks how the carbohydrate in foods affects blood sugar levels, based on testing in people. Relevance – The higher the glycemic index of a food, the more it would be expected to raise blood sugar after eating it. Foods with a lower glycemic index result in a gentler rise in blood sugar. Glycemic index values for foods are available on websites and in books.
Glycyrrhizin – Definition – Glycyrrhizin is a compound found in licorice that is responsible for the sweet taste of the root. Relevance – Glycyrrhizin has reportedly been linked to high blood pressure and edema, but licorice and glycyrrhizin are used to treat peptic ulcers and are thought to have anti-inflammatory effects.
GMO – Definition – Genetically modified organisms, or GMOs, are organisms or foods that have had foreign genes put into their genetic codes. Relevance – There is significant public concern over the presence of GM foods in the diet based on animal studies, but the FDA states that GM foods are generally regarded as safe; GM foods are also nutritionally comparable to conventional foods.
Gout – Definition – A type of arthritis in which crystals of uric acid, which may feel like shards of broken glass, deposit in joints and result in severe pain. Relevance – Gout is generally managed with medication and dietary changes to help reduce uric acid levels in the blood.
Greenhouse gases – Definition – Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide and methane, contributing to global warming. Relevance – Global warming may result in more severe weather, dirtier air and extinction of certain wildlife, among other problems.