Fruits and Prediabetes
Q: I have recently been diagnosed with prediabetes. Should I stop eating sugary fruits?
A: Richard Siegel, MD, co-director of the Diabetes and Lipid Center...
FDA Questions Claims on Dietary Supplements Marketed for Diabetes
The FDA and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) recently issued warnings to 10 companies regarding fraudulent marketing claims that their dietary supplements prevent, treat,...
Healthy Diet and Lifestyle to Sidestep Metabolic Syndrome
Three or more key factors add up to a higher risk for heart disease and diabetes. But healthy nutrition and exercise reverse the trend.
Debunking 6 Probiotic Myths
Some people use supplements and fermented foods containing probiotics-beneficial bacteria and yeasts-in an effort to improve health. But, is there good science behind them? Probiotic experts help clear up six common myths.
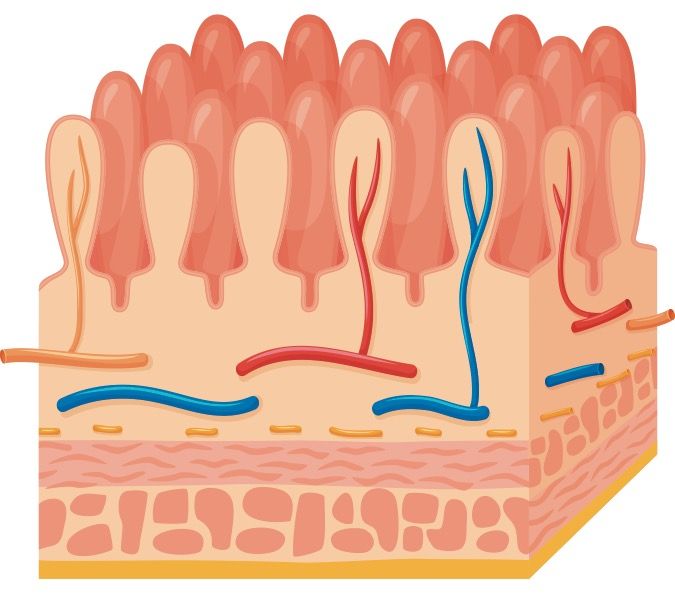
The Lowdown on Leaky Gut
As the popular depiction of leaky gut goes, damage to the lining of the small intestine can release undigested food particles, bacteria and toxins into your bloodstream. And, that can potentially spur a myriad of health problems ranging from digestive issues to joint pain. Without a doubt, this description is oversimplified and misleading. But, its worth looking at whether leaky gut-or more precisely, increased intestinal permeability-is a legitimate concern.
Cinnamon and Blood Sugar
Cinnamon has long done double duty in cooking and as a folk remedy for various ailments. Today, scientists are studying cinnamon to see if it improves blood sugar, particularly in type 2 diabetes.
Drink Coffee, Live Longer?
Some people view coffee as a guilty pleasure. But, research suggests drinking coffee may actually have some health benefits. That evidence includes two new, large observational studies of diverse populations published in the Annals of Internal Medicine. Both found drinking coffee was associated with a modestly (less than 20%) reduced risk of dying from various conditions, compared to not drinking coffee.
Vitamin D Fails to Improve Insulin Function
Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with increased diabetes risk. But, the few published small trials of vitamin D supplementation havent shown a benefit on insulin function, which is important in blood sugar control. Included in this list is a new trial in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Diet Causing 300,000+ Annual Cardiovascular & Diabetes Deaths
We're often told to eat better to ward off risk of disease and dying early. In that effort, knowing which eating habits to focus on could be helpful. Findings from a new study in JAMA show the large potential impact of 10 dietary factors on Americans' risk of dying from heart disease, stroke or type 2 diabetes. These three conditions encompass the term cardiometabolic disease.
Physical Activity Is Anti-Inflammatory
Physical activity is good for your heart, but why? A big reason may be its role in lowering inflammation.