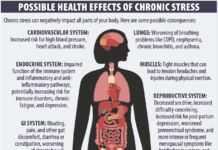
Reducing Sodium Intake Lowers High Blood Pressure–You Can Do It!
If you have high blood pressure, you’ve probably been told to decrease your intake of sodium (the major source of which is salt). Some...
Whole Grains Associated with Lower Risk for Type 2 Diabetes
A review and analysis of available research concluded that eating whole grains may help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The researchers...
Time-Restricted Eating Without Cutting Calories Does Not Lead to Weight Loss
Time-restricted eating (also called intermittent fasting) is a popular weight-loss strategy. A randomized controlled trial has found it only works to reduce weight if...
Data Suggest Any Activity is Better Than None for Stroke Prevention
The results of a meta-analysis suggest any amount of physical activity is better than none.
The review, which pooled results from 15 studies involving...
Eating More Frequently Does Not Impact Markers of Appetite or Inflammation
There are dietary recommendations for how many calories one should eat daily and what foods are the best choices to provide those calories, but...
Study Confirms Ultraprocessed Foods are Bad for Health
A recent study reviewed results from 45 pooled analyses on the health impacts of ultraprocessed foods (UPFs). Together, these studies include 9.9 million participants....
Data Suggest Any Activity is Better Than None for Stroke Prevention
The results of a meta-analysis suggest any amount of physical activity is better than none.
The review, which pooled results from 15 studies involving...
Recommendations to Limit Red Meat for Cardiovascular Health Upheld by Large Study
Dietary guidelines recommend limiting consumption of red meat (beef, pork, and lamb) to lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and generally support good health....
Mindfulness Training Can Help Improve Eating Patterns
It can be difficult to stick to dietary changes. A randomized controlled trial found that mindfulness training can help.
The study gave home blood-pressure monitoring...
Healthy Lifestyle May Support Better Brain Function—Even with Brain Changes Suggestive of Dementia
The Rush Memory and Aging Project gathered information on lifestyle and cognitive function for up to 24 years in a cohort of individuals and...