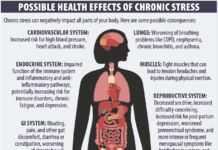
The Health Benefits of Strength Training
While aerobic activities like walking, jogging, gardening, swimming, and playing tennis or pickleball are an important part of a healthy lifestyle, there are many...
A Fiber-Rich Diet May Improve Response to Immunotherapy Cancer Treatment
Immunotherapy uses a person’s own immune system to fight cancer. One such treatment uses immune checkpoint inhibitors—medicines that target proteins that switch immune cells...
You’ve answered questions about oats before, but I’m unclear as to whether instant oats...
Judith C. Thalheimer, RD, LDN, managing editor of Tufts Health & Nutrition Letter, answers: “After the inedible husk is removed from an oat grain,...
What You Need to Know about Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men in the U.S. and around the globe. Worldwide, there are nearly a million new...
News Bites May 2022
Walking Can Preserve Women’s Muscle with Age, No Extra Protein Needed
A trial that asked if milk was better at helping build muscle than a...
Protect Yourself from Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States. Following screening recommendations is essential to prevention, but lifestyle...
Lose Excess Weight to Fight Breast Cancer
Women, if you are looking for more motivation to have a healthy weight, a new study published in the Journal of the National Cancer...
Cancer Risk and Sedentary Behavior
A study published recently in JAMA Oncology found that greater sedentary time was associated with higher cancer mortality. This prospective cohort study followed 8,002...
Cancer and Diet: The Latest in Prevention
Cancer is the second leading cause of mortality in the United States, accounting for one in four deaths. Lifestyle choices such as use of...
Obesity Increases Cancer Risk
A new report from the World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) links obesity to 12 types of cancer. The report, Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity and Cancer: a Global Perspective, analyzed a decade of research to develop cancer prevention recommendations. The analysis found strong evidence that being overweight or obese throughout adulthood increases risk of cancer of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, gallbladder, liver, colon, breast (post menopause), ovaries, endometrium, prostate (advanced), and kidney.