Healthy Fats Reduce Diabetes Risk
Swapping healthy unsaturated fats for carbohydrates or saturated fats may reduce your risk of diabetes, according to a new analysis of 102 randomized trials totaling 4,660 participants.
Heart Benefit Seen from Compound in Tea, Cocoa, Apples
A study of older Dutch men provides new insight into why tea and cocoa protect against heart disease, showing for the first time that a compound called epicatechin is associated with reduced mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Blood Levels of Omega-3s from Fish, Plants Linked to Lower Fatal Heart Risk
An analysis of 19 studies involving 45,637 participants in 16 countries provides the most comprehensive picture to date of how omega-3 fats may influence heart disease. Higher blood levels of omega-3s from seafood as well as plants were associated with a lower risk of dying from heart attacks
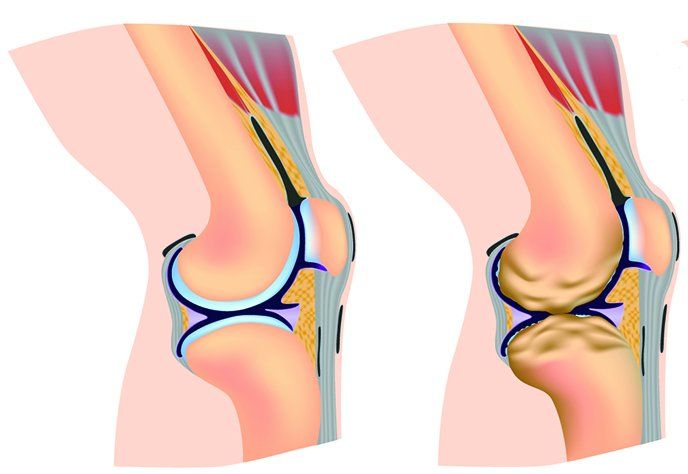
Smart Fat Choices Might Slow Arthritis Progression
What's good for your heart might also be good for your aching knees. High intakes of saturated fat were associated with a faster progression of knee osteoarthritis in a new prospective observational study, while consuming more heart-healthy unsaturated fats was linked to slower progression.
Are You Getting Enough Fiber?
An important nutrient for reaching old age free of disease and disability might surprise you. According to a new Australian study, it's dietary fiber - a nutrient that, by definition, you don't even digest. In its path through your body, however, fiber is associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and some cancers.
Omega-6s in Vegetable Oil Linked to Lower Diabetes Danger
Contrary to some advice to limit the omega-6 fats found in vegetable oil, a new Finnish study finds that high blood levels are associated with a significantly reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, at least in men. The study looked primarily at linoleic acid, an essential omega-6 fat not formed by the body, which must be obtained from the diet. It's the primary fatty acid found in oils high in polyunsaturated fats as well as nuts and seeds.
FDA Updates Nutrition Labels
After a two-year review period, the US Food and Drug Administration formally adopted changes to the Nutrition Facts panels that appear on some 800,000 food products. The updated labels will be required on products by July 26, 2018, except for small producers who will get an extra year to comply.
What is the Right Menu to Control Hypertension?
If you're worried about high blood pressure, a new systematic review of scientific evidence has good news: Changing your diet really can make a difference. Not surprisingly, the most effective diet for reducing hypertension was one designed specifically for that purpose - the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) plan. But other interventions, including cutting salt and calories, also were associated with blood-pressure benefits.
Fish Linked to Less Alzheimers Disease in Those Most at Risk
If concerns about mercury in seafood have kept you from the possible brain benefits of consuming more fish, an unusual new study has good news. Researchers did find that older adults who ate more seafood had higher brain levels of mercury - but that toxin was not associated with any signs of dementia. On the other hand, people at greatest genetic risk for Alzheimer's who consumed the most seafood showed less evidence of the diseases damage in the brain.
92% of Restaurant Meals Too High in Calories
If you're eating out often, you're probably overdoing calorie consumption - even if you avoid fast-food restaurants. Meals consumed at fast-food restaurants have been singled out as culprits in America's obesity epidemic. But a new study reports that both chain and local restaurants are routinely serving far more than should be consumed in a single meal - often more than you should eat in a whole day.