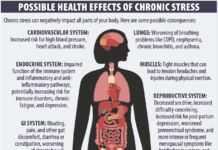
New Tufts research has linked low blood levels of vitamin B6 to markers of inflammation that contribute to heart disease and other chronic conditions. Previous studies have associated low B6 levels with specific signs of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). But Lydia Sakakeeny, PhD, in Tufts HNRCA Vitamin Metabolism Laboratory, and colleagues said this was the first large-scale study to find an association between vitamin B6 and a wide range of markers for inflammation.

Sakakeeny and colleagues from Tufts, Boston University and Safra Childrens Hospital analyzed data on 2,229 men and women from the Framingham Offspring study. The researchers found that levels of PLP, an indicator of vitamin B6 levels in the blood, correlated with a score for 13 different markers of inflammation. As vitamin B6 levels rose, indicators of inflammation tended to drop; on the other hand, people with lower B6 levels were more likely to show signs of inflammation.
The same associations werent seen with other B vitamins, suggesting a specific link to vitamin B6. As an observational study, however, the research couldnt prove cause and effect, or even the direction of causality.
Low vitamin B6 status, based on plasma concentrations of PLP, has been identified in inflammatory diseases, including cardiovascular disease, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and diabetes, Sakakeeny and colleagues noted in the Journal of Nutrition.
That doesnt mean, however, that you should stock up on B-vitamin supplements; in fact, taking large doses of B6 has been shown to cause tingling sensations, difficulty walking and even nerve damage. (The tolerable upper intake level for vitamin B6 is 100 milligrams daily for adults.) Eating a healthy diet should put plenty of good sources of vitamin B6 on your plate, such as lean poultry, fish, legumes, red peppers, potatoes and other starchy vegetables, and fruits other than citrus. (See box.)
| B6 Basics |
Most adults need 1.3 mg daily of vitamin B6 until after age 50, when the recommended amount goes up to 1.5 mg for women and 1.7 mg for men. Good food sources of vitamin B6 include:
| Chickpeas, canned, 1 cup | 1.1 mg |
| Tuna, yellowfin, fresh, cooked, 3 oz | 0.9 mg |
| Salmon, sockeye, cooked, 3 oz | 0.6 mg |
| Chicken breast, roasted, 3 oz | 0.5 mg |
| Breakfast cereals, fortified | 0.5 mg |
| Potatoes, boiled, 1 cup | 0.4 mg |
| Banana, 1 medium | 0.4 mg |
| Ground beef, 85% lean, broiled, 3 oz | 0.3 mg |
| Sweet red pepper, 1/2 cup | 0.2 mg |
| Bulgur, cooked, 1 cup | 0.2 mg |
| Cottage cheese, 1% low-fat, 1 cup | 0.2 mg |
| Winter squash, baked, 1/2 cup | 0.2 mg |
The next step is determining the mechanism of the relationship between B6 and inflammation, Sakakeeny cautioned. From there, it then may lead to new treatments or dietary recommendations.
TO LEARN MORE: Journal of Nutrition, July 2012; abstract at dx.doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.153056. Vitamin B6 QuickFacts ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-QuickFacts.