You may not have to go heavy on the cocoa to boost your brain. Previously, a special cocoa high in flavanols was shown to positively affect cognitive function in older adults with early memory decline.
But now a new study conducted in older adults with hypertension and/or diabetes has found that drinking just two cups a day of cocoa for a month was associated with significant improvements in cognitive function and blood flow in the brain.
Thinkstock
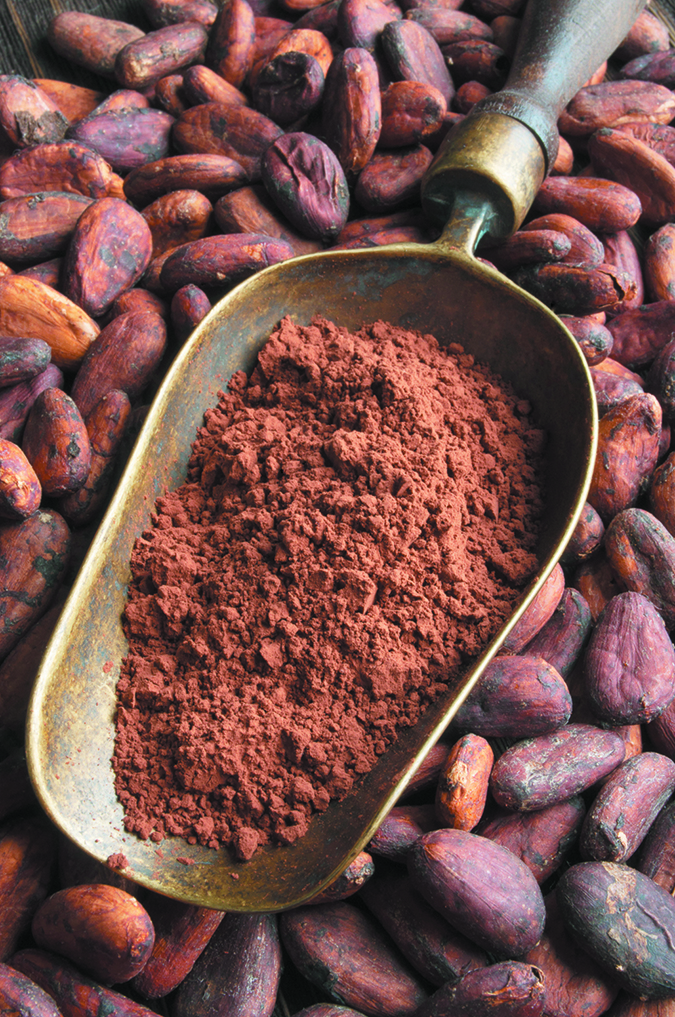

Higher levels of flavanols—the antioxidant compounds credited with cocoa and dark chocolate health benefits—made no difference. Overall, however, participants saw brain benefits once they started drinking either flavanol-enhanced cocoa or a lower-flavanol cocoa.
“Researchers are still trying to discover the optimal intake of flavanols,” comments Jeffrey B. Blumberg, PhD, director of Tufts’ HNRCA Antioxidants Research Laboratory. “That dose, along with different durations of consumption, may likely differ depending on factors like age, sex and health status. Also, the possibility should be considered that some of this apparent benefit may be derived from other bioactive compounds in cocoa.”
COCOA BEAN BEFEFITS: The flavanols found in cocoa and dark chocolate are part of a larger group of compounds called flavonoids that occur naturally in plant foods—in this case, the cocoa bean from which cocoa and chocolate are made. Flavanols are also found in red wine and tea. The flavanols in the cocoa bean, however, are a unique mixture of these phytonutrients. Scientists have found that cocoa flavanols positively affect the circulatory system and help maintain the flexibility of arteries. While this is obviously important to heart health, your brain also depends on adequate blood flow to function.
In the new study, published in Neurology, Farzaneh A. Sorond, MD, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and colleagues tested the effects of cocoa consumption on 60 volunteers, average age 73. Although none had dementia, 17 suffered from a condition called impaired neurovascular coupling (NVC), a measure of blood flow in the brain as it relates to nerve cells (neurons). Researchers initially tested two levels of flavanols in cocoa, consumed twice a day for 30 days. Participants were encouraged to alter their diets to compensate for the extra calories in the cocoa.
No significant difference was seen between the two types of cocoa, so the results from both groups were merged. Participants free of impaired NVC showed no significant benefits from cocoa consumption.
But the small group of volunteers with impaired NVC saw dramatic changes after just a month of cocoa intake. Neurovascular coupling improved by more than double, and scores on standard cognitive tests jumped 30%.
BETTER BLOOD FLOW: Indications that cocoa flavanols might improve blood-vessel function in the brain were further supported by data from several other studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). Researchers from the University of Nottingham Medical School in the UK reported findings that cocoa consumption resulted in increased blood flow to areas of the brain.
Lead scientist Ian A. Macdonald, PhD, commented, “This raises the possibility that certain food components like cocoa flavanols may be beneficial in increasing brain blood flow and enhancing brain function among older adults or for others in situations where they may be cognitively impaired, such as fatigue or sleep deprivation.”
Should you start sipping cocoa to support your brain? Tufts’ Blumberg advises, “The available evidence about the potential benefits of cocoa on the brain is far too limited to make any recommendations. However, it is noteworthy that the EU Commission recently approved a health claim that 200 milligrams of cocoa flavanols can ‘help maintain the elasticity of blood vessels, which contributes to normal blood flow.’ This dose is equivalent to 2.5 grams high-flavanol cocoa powder or 10 grams of high-flavanol dark chocolate (about one-fifth of a regular size chocolate bar).”





















I want to thank sharing such a good incredible article. This specific is quite a good
piece, I feel just like very few people manage to express their view thus clearly.
But just you and https://solothurnclassics.ch/the-great-gaming-debate-ps4-or-the-ipad/ do it in a way that touches the reader’s soul.