Organic Crops Found Higher in Antioxidants
Are organic fruits, vegetables and grains better for you? No one disputes that organic foods are lower in synthetic pesticides, though how important that is to your health remains controversial, as long as levels fall below EPA thresholds. But most studies have found little difference between organic and conventionally grown crops in nutritional value.
Reality Check on Resveratrols Health Benefits
Proponents of resveratrol, the antioxidant compound found in red wine and grapes whose near-miraculous health claims have created a $30 billion supplement industry, must have felt a bit of whiplash lately. First, a new study of dietary intake of resveratrol in the Chianti wine-making region of Italy made headlines by reporting no correlation with longevity or lower risks of cancer or cardiovascular disease. Resveratrol Health Benefits a Myth?, one news article asked. Then, just three weeks later, another new study reported that resveratrol supplements improved memory in overweight older people-raising hopes once again.
Green Tea May Enhance Working Memory
A small clinical trial suggests that green tea could improve the connectivity between parts of the brain involved in tasks of working memory. You might think of working memory as the brains sticky notes, where bits of information are temporarily held for manipulation before forgetting or transferring to long-term memory.
How to Get Maximum Health Benefits from Tomatoes
Tomatoes are so ubiquitous in the American diet, from the fresh tomatoes just now coming into prime season to countless processed products, that its hard to believe they were once commonly avoided as poisonous. Its true that tomatoes, like potatoes and peppers, belong to the nightshade family, and their leaves contain alkaloids that can indeed be toxic to pets. Europeans who saw the plants from the New World thought tomatoes resembled belladonna-deadly nightshade-and gave the fruit the forbidding name wolf peach.
Q. I keep seeing advertisements for multivitamins that say I need antioxidants to promote...
Q. I keep seeing advertisements for multivitamins that say I need antioxidants to promote cell health. What does this mean?
Large Study Will Test Chocolate Compounds
Participants in a recently announced nationwide study wont get to eat chocolate candy in the name of science, but they will be testing the cocoa flavanols thought to give dark chocolate heart-healthy properties. The four-year study will give participants either a placebo or flavorless capsules containing doses of cocoa flavanols higher than could be easily obtained by eating chocolate. It will be by far the largest trial of the chocolate compounds, which previous findings have…
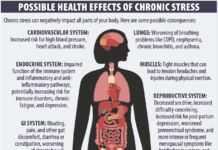
The Heart-Brain Blood Supply
Just like every other organ and tissue in the body, the brain needs oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to function properly. Because the brain is so crucial to the bodys survival, it receives a disproportionate amount of blood. Though it takes up only about 2 percent of the bodys weight, the brain receives 15 to 20 percent of the bodys entire blood supply, and 25 percent of its oxygen supply. The body will deprive other parts of the body of blood to ensure that the brain has what it needs.
The heart feeds the brain by sending blood through vessels both on the surface of the brain and deep inside it. Two pairs of arteries branching out from the aorta-the internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries-supply the brain with blood. Carotid arteries send blood to the front of the brain, and vertebral arteries send blood to the back of the brain.
Blood flow into the brains tissues is a bit different than it is in other parts of the body. Elsewhere in the body, nutrients, oxygen and waste products can move freely in and out of the capillaries. This is not true in the brain. The brain has its own checkpoint, the blood-brain barrier, a semi-permeable system that lets only certain substances pass into the brain. This barrier protects the brain against viruses, toxins, hormones, and other substances in the blood that might harm the brains delicate tissues.
Considering how essential nutrient-rich blood is to the brains function, any disruption in blood flow can pose a serious risk. A blockage in the brains blood supply from a clot either in the brain or from elsewhere in the body is called a stroke. A stroke deprives the affected part of the brain of oxygen. Without oxygen, the brains cells will die. If too many brain cells die, thought and virtually every other function will come to a halt. Two primary risk factors for stroke are high blood pressure and heart disease, which illustrates the close relationship between heart and brain health.
For more information on the connection between the heart and brain, purchase Heart-Brain Diet: Essential Nutrition for Healthy Longevity by Tufts Medical Report.
The heart feeds the brain by sending blood through vessels both on the surface of the brain and deep inside it. Two pairs of arteries branching out from the aorta-the internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries-supply the brain with blood. Carotid arteries send blood to the front of the brain, and vertebral arteries send blood to the back of the brain.
Blood flow into the brains tissues is a bit different than it is in other parts of the body. Elsewhere in the body, nutrients, oxygen and waste products can move freely in and out of the capillaries. This is not true in the brain. The brain has its own checkpoint, the blood-brain barrier, a semi-permeable system that lets only certain substances pass into the brain. This barrier protects the brain against viruses, toxins, hormones, and other substances in the blood that might harm the brains delicate tissues.
Considering how essential nutrient-rich blood is to the brains function, any disruption in blood flow can pose a serious risk. A blockage in the brains blood supply from a clot either in the brain or from elsewhere in the body is called a stroke. A stroke deprives the affected part of the brain of oxygen. Without oxygen, the brains cells will die. If too many brain cells die, thought and virtually every other function will come to a halt. Two primary risk factors for stroke are high blood pressure and heart disease, which illustrates the close relationship between heart and brain health.
For more information on the connection between the heart and brain, purchase Heart-Brain Diet: Essential Nutrition for Healthy Longevity by Tufts Medical Report.
Q. How much green tea should one consume daily to get the benefits I...
A. Jeffrey Blumberg, PhD, director of Tufts HNRCA Antioxidants Research Laboratory, answers: The health benefits associated with drinking tea (green, oolong or black) are...
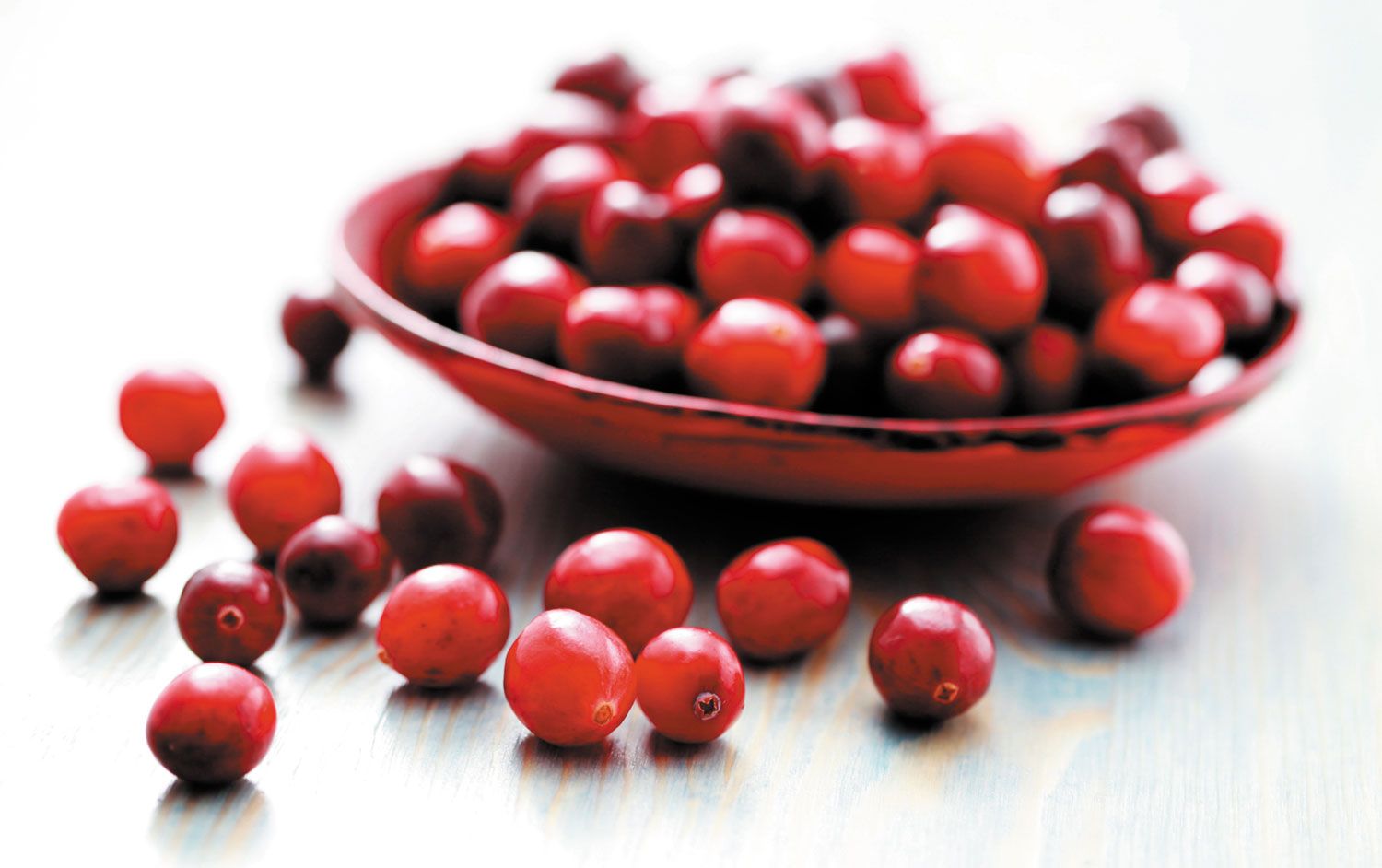
Cranberries: Theyre Not Just for Thanksgiving Anymore
If you think of cranberries as strictly Thanksgiving fare, you're missing out on the unique health benefits of this tart red fruit. "The profile of cranberries' biologically active constituents is distinct from that of other berry fruit," says Jeffrey B. Blumberg, PhD, director of Tufts' HNRCA Antioxidants Research Laboratory. Blumberg and colleagues recently authored a comprehensive review of cranberries' bioactive compounds and their effects on human health, published in Advances in Nutrition.
Antioxidants Vary in Green Tea
Green tea is touted for its health-promoting properties in large part because of its high levels of antioxidants called catechins, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG).